A high-risk pregnancy is one in which the mother, baby, or both are at an increased risk of complications before, during, or after delivery. Certain health conditions, lifestyle factors, or pregnancy-related issues can elevate the risk level, requiring special monitoring and care from healthcare providers.
Common Reasons for High-Risk Pregnancy:
1. Maternal Age
2. Pre-existing Health Conditions
3. Pregnancy-Related Complications
4. Lifestyle Factors
5. History Factors


Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive a child after 12 months (or 6 months if the woman is over 35) of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse.
🔍 Types of Infertility:
Primary infertility – When a couple has never been able to conceive.
Secondary infertility – When a couple has had at least one successful pregnancy but is now unable to conceive again.
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It causes a range of symptoms related to hormonal imbalance, irregular ovulation, and metabolism, and is one of the leading causes of infertility.
⚠️ Common Symptoms:
● Irregular or missed periodsIrregular or missed periods
● Difficulty getting pregnant
● Excess hair growth (face, chest – hirsutism)
● Darkening of skin, especially around neck or underarms
● Weight gain or difficulty losing weight


Complete Gynecological & Obstetric Care refers to comprehensive medical services that address a woman's reproductive health needs through all stages of life—from adolescence to pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause.
👩⚕️ Gynaecological Care Includes:
● Menstrual problems (irregular, painful, or heavy periods)
● PCOS and hormonal imbalances
● Pelvic pain & infections
● Fibroids, cysts, and endometriosis etc....
🤰 Obstetric Care Includes:
● Preconception counseling
● Antenatal care (during pregnancy)
● Labour & Delivery support
● Postnatal care
Fetal Medicine (also known as Maternal-Fetal Medicine) is a specialized branch of obstetrics that focuses on the health of the unborn baby (fetus) and the management of high-risk pregnancies. It involves advanced monitoring, diagnosis, and treatment of fetal conditions while the baby is still in the womb.
👶 What Does Fetal Medicine Involve?
🩺 Prenatal Screening & Diagnosis
👩⚕️ Management of High-Risk Pregnancies
⚕️ Fetal Therapy (if required)


Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s menstrual cycles. It is officially diagnosed when a woman has not had a period for 12 consecutive months, and it typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, though the age can vary.
🌸 Common Symptoms:
● Hot flashes and night sweats
● Irregular or missed periods (during perimenopause)
● Mood swings, irritability, anxiety
● Vaginal dryness and discomfort
● Sleep disturbances
● Weight gain, especially around the abdomen
● Decreased libido
● Memory issues or trouble concentrating
Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting a woman’s reproductive organs — such as the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes.
Instead of a large abdominal incision, the surgeon makes small keyhole cuts and uses a laparoscope (a thin, lighted camera) to perform the procedure with precision.
✅ Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery:
● Smaller incisions → Less pain
● Faster recovery time
● Minimal scarring
● Shorter hospital stay
● Sleep disturbances
● Lower risk of infection or complications

Recurrent Pregnancy Losses (RPL) refer to the occurrence of two or more consecutive miscarriages, usually before the 20th week of pregnancy. It is a distressing condition that affects around 1–2% of couples trying to conceive.
🧬 Causes of Recurrent Pregnancy Loss:
1. Genetic Factors
2. Uterine Abnormalities
3. Hormonal Imbalances
4. Blood Clotting Disorders (Thrombophilia)
5. Infections
6. Immune System Issues
7. Lifestyle & Environmental Factors
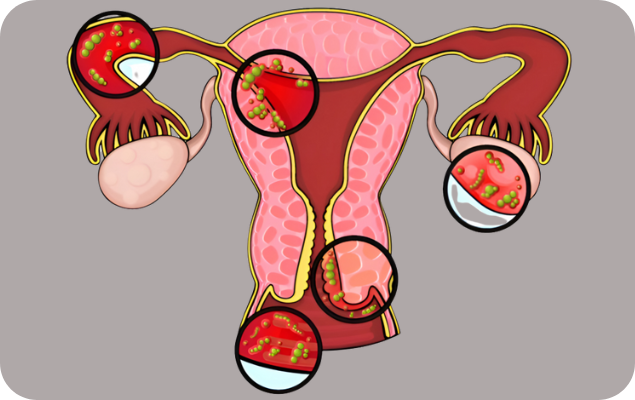
Reproductive Tract Infections (RTIs) are infections that affect the reproductive organs in both men and women. These can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, and may involve the lower tract (vagina, cervix, urethra) or the upper tract (uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries).
🔍 Types of Reproductive Tract Infections (RTIs):
1. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
2. Iatrogenic Infections
3. Endogenous Infections
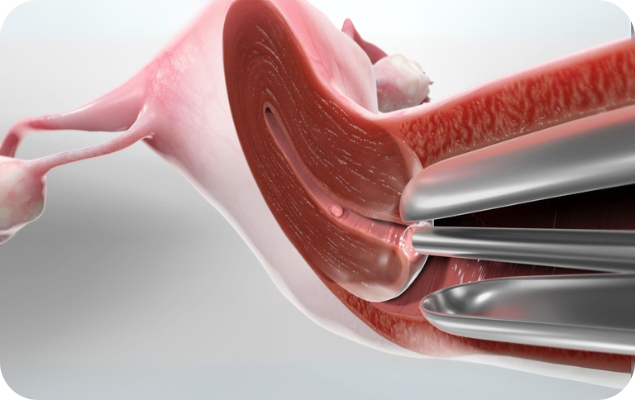
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine the inside of the uterus (womb). It allows a gynecologist to diagnose and treat uterine problems using a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope, which is inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus.
🔍 Why Is Hysteroscopy Done?
● Abnormal uterine bleeding
● Repeated miscarriages
● Infertility evaluation
● To locate and assess uterine abnormalities (polyps, fibroids, septum)
● Removal of polyps or fibroids
● Removal of adhesions (scar tissue)
● Treatment of uterine septum
● Endometrial ablation (to treat heavy periods)
Major Gynaecological Operations are surgical procedures performed to treat complex or serious conditions affecting the female reproductive system, such as the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, or cervix. These surgeries are usually done in a hospital setting and may require general anesthesia and a longer recovery time compared to minor procedures.
🏥 Common Major Gynaecological Surgeries:
1. Hysterectomy
2. Myomectomy
3. Ovarian Cystectomy
4. Salpingectomy / Salpingo-oophorectomy
5. Endometriosis Surgery
6. Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery
7. Cancer Surgeries
8. Tubal Reanastomosis
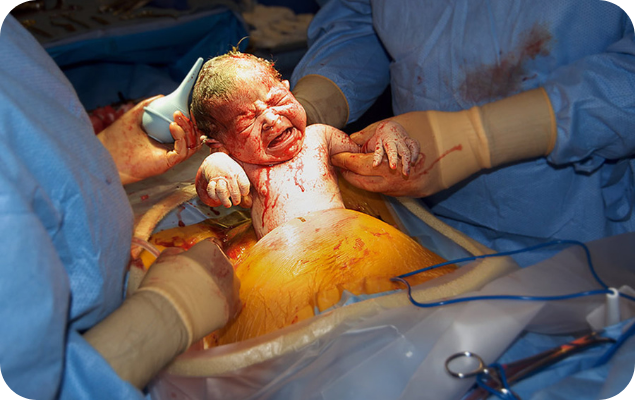
A C-section delivery (Cesarean section) is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through incisions made in the mother's abdomen and uterus. It is an alternative to vaginal birth, performed when it is considered safer for the mother, baby, or both.
🔍 Common Reasons for a C-Section:
● Baby in breech or abnormal position
● Placenta previa (placenta blocking the cervix)
● Fetal distress
● Multiple pregnancy (twins, triplets)
● Previous C-section or uterine surgery
● Prolonged or stalled labor
● Large baby (macrosomia)
● Maternal health issues (e.g., high blood pressure, infections)
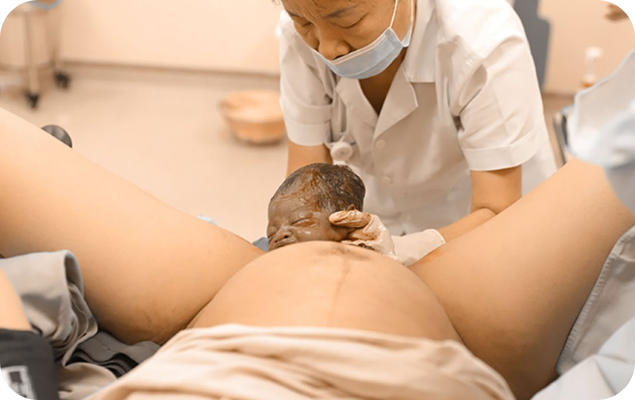
Vaginal Delivery is the natural method of childbirth, where the baby is born through the birth canal (vagina). It is the most common and preferred method of delivery when there are no medical complications, as it involves shorter recovery time and fewer risks compared to surgical alternatives.
✅ Benefits of Vaginal Delivery:
1. Faster recovery (usually within 1–2 weeks)
2. Lower risk of infection and complications
3. Earlier bonding and breastfeeding
4. Shorter hospital stay
5. Beneficial to the baby's immune and respiratory systems (exposure to birth canal bacteria)
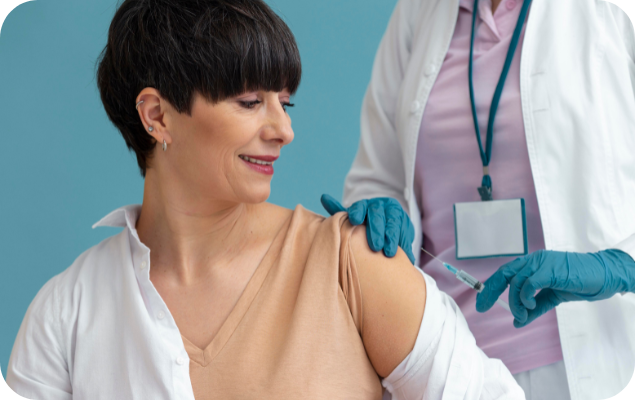
The Cervical Cancer Prevention Vaccine—commonly known as the HPV vaccine—protects against infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is the leading cause of cervical cancer.
🛡️ Why Get the HPV Vaccine?
● Prevents up to 90% of cervical cancer cases
● Also protects against precancerous cervical lesions
● Reduces risk of other HPV-related cancers and genital warts
Girls' Adolescent Health refers to the physical, emotional, and reproductive well-being of girls aged roughly 10 to 19 years, a period of rapid growth, hormonal changes, and identity development. Ensuring good health during adolescence lays the foundation for a healthy adulthood.
🧕 Why Is Adolescent Health Important?
● Prevents long-term health issues
● Encourages body positivity and confidence
● Reduces risk of early pregnancy and reproductive issues
● Builds a strong foundation for adult health and well-being


Urogynaecology (or Urogynecology) is a specialized branch of gynaecology that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of pelvic floor disorders in women. These conditions often involve the bladder, uterus, vagina, and rectum, especially after childbirth, surgery, or with aging.
🔍 What Conditions Do Urogynaecologists Treat?
1. Urinary Incontinence
2. Pelvic Organ Prolapse
3. Overactive Bladder (OAB)
4. Fistulas
5. Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)e
6. Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis
7. Bowel Control Problems (Fecal Incontinence)